14TH FEBRUARY, ISRO MISSION

The Indian Space Research Organisation is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman of ISRO acts as the executive of DOS as well. ISRO is the primary agency in India to perform tasks related to space-based applications, space exploration, and the development of related technologies. It is one of six government space agencies in the world that possess full launch capabilities, deploy cryogenic engines, launch extra-terrestrial missions and operate large fleets of artificial satellites.

The Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established by Jawaharlal Nehru under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) in 1962, on the urging of scientist Vikram Sarabhai recognizing the need in space research. INCOSPAR grew and became ISRO in 1969, within DAE. In 1972, the Government of India had set up a Space Commission and the Department of Space (DOS), bringing ISRO under the DOS. The establishment of ISRO thus institutionalized space research activities in India. It since then has been managed by the DOS, which governs various other institutions in India in the domain of astronomy and space technology.
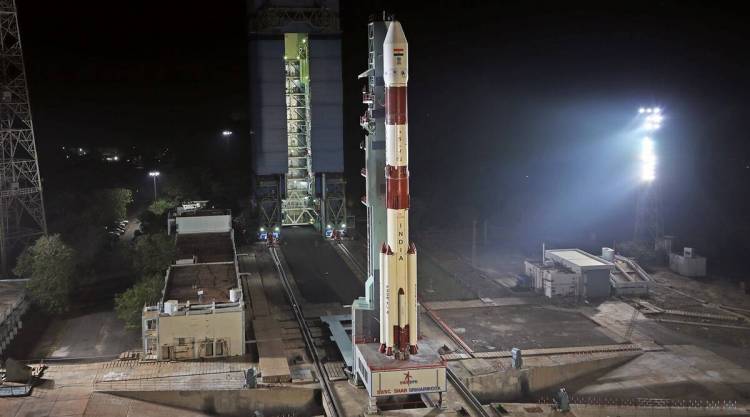
The countdown for this year’s first launch by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will begin early on Sunday morning, with takeoff scheduled for India’s workhorse Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C52) from Andhra Pradesh’s Sriharikota at 5 am on February 14.
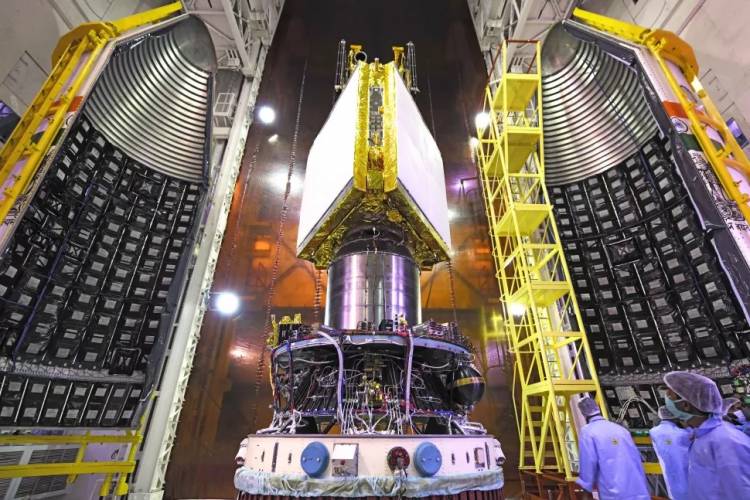
PSLV will carry a radar imaging earth observation satellite, called the EOS-04, as its main payload. Along with this, the launch vehicle will host a technology demonstration thermal imaging satellite and a student-developed satellite with two scientific instruments.
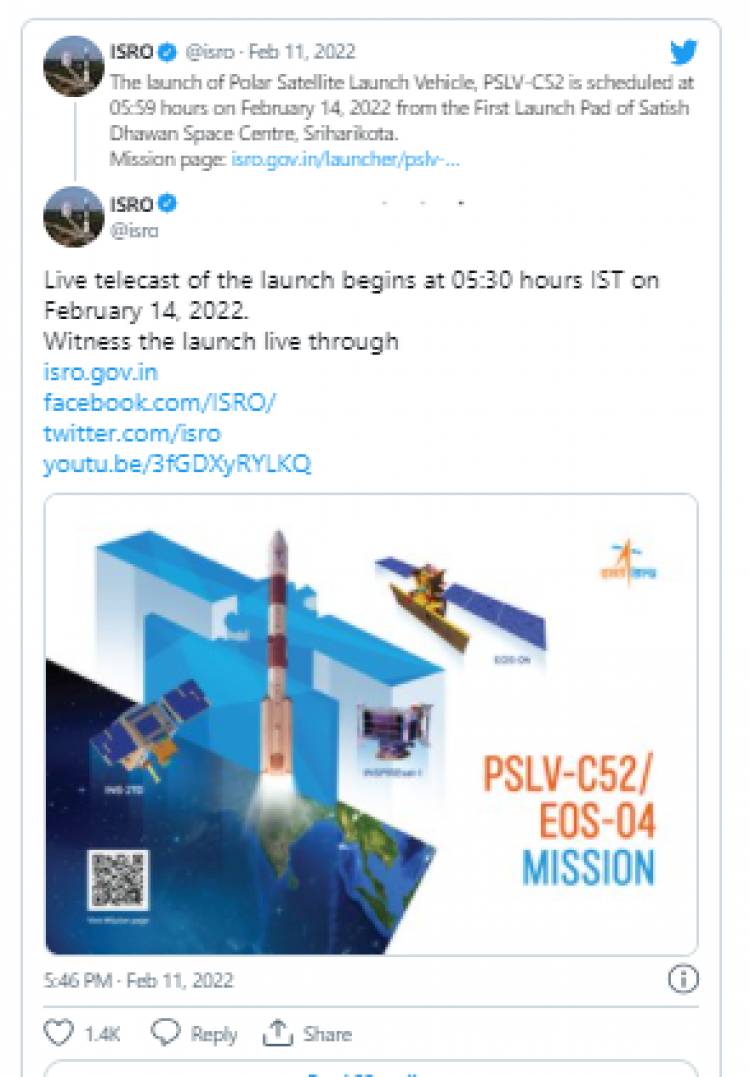
The PSLV-C52/EOS-04 mission has been delayed twice already due to the pandemic. Initially planned for the third quarter of 2021, the launch got pushed to the fourth quarter and finally to early 2022.
The mission is also a first for newly appointed ISRO chief S Somanath. He took over as the head of the Indian space agency last month.
“The countdown process of 25 hours and 30 minutes leading to the launch would commence at 04:29 hours on February 13, 2022, after authorization by the Launch Authorization Board,” ISRO said in a statement on Saturday.
Monday’s launch, if successful, will also be a boost for the agency. ISRO’s last mission – the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV-F10), carrying another earth observation satellite EOS-03, failed in August last year due to a technical error.
The PSLV-C52 mission — expected to last 33.5 minutes — will carry the 1,700kg EOS-04 satellite to the sun-synchronous polar orbit, some 529 km from the Earth’s surface.
You can watch the launch of the EOS-04 satellite live on Sunday (Feb. 13) at 7:29 p.m. EST (0029 GMT or 6:29 p.m. local time Monday, Feb. 14), assuming that the mission blasts off on time. You can watch the launch live on this page, as well as on the ISRO website and YouTube Channel. The Livestream generally turns on a few minutes before launch.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3fGDXyRYLKQ&t=1s
A sun-synchronous polar orbit is an orbit in which the satellite passes over the Earth’s poles but also remains in the same position relative to the Sun. It allows a satellite to pass over a particular location, such as India, at a fixed time every day. The EOS-04 satellite is a radar imaging satellite capable of providing high-quality images under all weather conditions. It can be used to capture images for agriculture, forestry, flood mapping, soil moisture, and hydrology. The spacecraft will also carry the INS-2DT technology demonstrator satellite – which has a thermal imaging camera and can help in the assessment of land and water surface temperatures apart from mapping vegetation. The third key component for the mission is the InspireSat-1 satellite developed by the Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, University of Colorado-USA, Nanyang Technological University-Singapore, and National Central University-Taiwan. This satellite will use two instruments to study ionosphere dynamics and the Sun’s coronal heating process.

The PSLV launch will be witnessed by the chairperson-designate of the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe) – an independent body under the Department of Space that will be responsible for overseeing the activities of private-sector space companies.
“Excited about physically witnessing my first rocket launch on Monday morning. PSLV is India’s workhorse launch vehicle with more than 50 successful missions. Yet every launch is a new launch. I have now witnessed up close what goes behind preparing for a successful launch,” said Dr. Pawan Goenka, former managing director of Mahindra and Mahindra who was appointed as the IN-SPACe chairperson-designate last year.
If you liked this post, I’d be very grateful if you’d help it spread by emailing it to a friend or sharing it on Twitter or Facebook. Do not forget to like us on Facebook and follow us on Instagram. Send your entries too…
Thank You
Aashi Harita























Comments (0)